Exudative AMD refers to the disease process in AMD whereby choroidal neovascularisation (CNV) develops and grows through defects in Bruch's membrane into the sub-RPE or subretinal spaces.
CNV carries the likelihood of leakage, leading to RPE 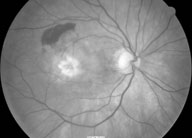 detachment, subretinal haemorrhage or lipid, and ultimately disciform scarring and central blindness.
detachment, subretinal haemorrhage or lipid, and ultimately disciform scarring and central blindness.
For further description, see 'Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) - classification' (Optician, February 3).
SYMPTOMS
Exudative AMD may cause profound central visual impairment.
SIGNS AND CLASSIFICATION
Exudative AMD was classified by the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) research group as Levels 4 and 5 in their classification for AMD:
Level 4 Advanced: choroidal neovascularisation, other exudative maculopathy, or geographic atrophic maculopathy in one eye but not the other. These forms of AMD carry a high risk of sudden, severe, central vision loss
Level 5 The most severe form of AMD is bilateral advanced AMD. In more than 40 per cent of patients with exudative AMD, the condition becomes bilateral within five years.
Register now to continue reading
Thank you for visiting Optician Online. Register now to access up to 10 news and opinion articles a month.
Register
Already have an account? Sign in here
